Infertility is such a personal, and usually so complicated, hurdle for so many couples. Lifestyles, age, and disease are all contributors that are easily recognized, yet there’s interest in another extremely important question that’s emerging now: Is infertility hereditary? That is to say, do genetics have any influence on if you or your partner can produce a child normally?
In this blog post, we’ll discuss how genetics can affect fertility in men and women. We’ll cover typical hereditary conditions associated with infertility, symptoms to look out for, and when to seek genetic testing. Whether you’re starting your fertility journey or experiencing unexplained infertility, knowing the genetic aspect can empower you with the right information and tools.
Understanding the Genetics of Infertility
What Are Genetic Causes of Infertility?
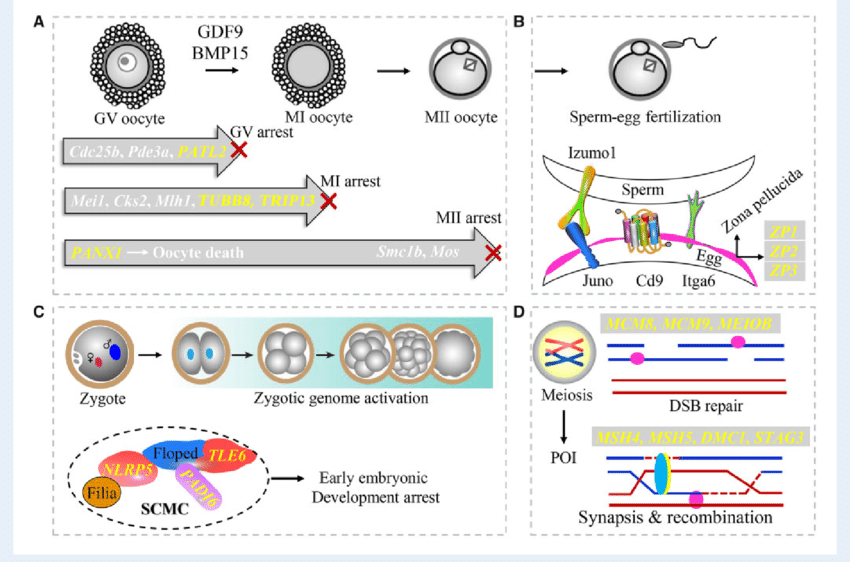
Genetic infertility is caused by genetic abnormalities or defects in chromosomes or individual genes. They might impair hormone levels, gamete formation (eggs or sperm), or viability of the embryo.
Some people have genetic mutations or chromosomal differences that do not impact their everyday health but can impact reproduction.
How Genetics Influence Female Fertility
1. Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Turner Syndrome: A condition where a woman lacks part or all of one X chromosome. This tends to result in ovarian failure.
- Fragile X Syndrome: Women with a premutation in the FMR1 gene can have early menopause or reduced ovarian reserve.
- Balanced Translocations: When chromosomes exchange pieces without losing or gaining genetic material, fertility can still be affected due to disrupted embryo formation.
2. Inherited Hormonal Disorders
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Although not entirely genetic, PCOS tends to run in families and can affect ovulation.
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH): Infrequent inherited condition that alters adrenal hormone production and can affect fertility.
Genetic Causes of Male Infertility
1. Y Chromosome Microdeletions
Some areas of the Y chromosome are absolutely necessary for the production of sperm. Microdeletions of these areas (particularly AZFa, AZFb, or AZFc) may result in:
- Azoospermia (absence of sperm in the semen)
- Severe oligospermia (extremely low sperm count)
These disorders can be inherited to male children if assisted reproductive methods are employed.
2. Klinefelter Syndrome (47, XXY)
Men with Klinefelter syndrome possess an extra X chromosome, resulting in:
- Poor testosterone production
- Small testes
- Low or absent sperm count
Some men can still have children with the help of advanced reproductive methods.
3. Cystic Fibrosis Gene Mutation
Men with congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD), a condition linked to cystic fibrosis gene mutations, can be healthy but ejaculate no sperm.
Trinity IVF Ahmedabad offers state-of-the-art diagnostic services to assess these genetic conditions and recommend personalized treatment.
Can Infertility Be Passed On?
The short answer: It depends on the cause.
- Monogenic Disorders (resulting from a mutation in a single gene) can be inherited in an autosomal dominant, recessive, or X-linked manner.
- Multifactorial Conditions, such as endometriosis or PCOS, have both genetic susceptibility and environmental factors.
- Chromosomal Disorders, such as balanced translocations, can be inherited or cause miscarriages or birth defects.
If either the man or woman has a history of reproductive problems in their family, a consultation with a fertility specialist or genetic counselor is recommended.
When to Have Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is not required for all couples. You might, though, gain from testing if:
- You’ve had repeated miscarriage
- There’s a family history of genetic illness or infertility
- You’re having IVF with recurrent implantation failures
- One of you has been diagnosed with a chromosomal abnormality
- You’re looking at using donor gametes or preimplantation genetic testing (PGT)
At Trinity IVF, we provide genetic screening and counseling to enable the identification of inherited causes and enhance treatment outcomes.
Types of Genetic Testing for Infertility
These are the most prevalent genetic tests employed in fertility treatment:
1. Karyotyping
It examines the number and arrangement of chromosomes in both partners. It’s employed to identify translocations, inversions, or missing chromosomes.
2. Y Chromosome Microdeletion Testing
For men with low or no sperm, it can detect deletions that impair sperm production.
3. CFTR Gene Testing
Checks for cystic fibrosis gene mutations that may cause CBAVD in males or carrier status in females.
4. FMR1 Gene Testing
Evaluates risk for Fragile X syndrome and premature ovarian failure in females.
5. Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
PGT is performed during IVF to test embryos for genetic defects prior to implantation. It involves:
- PGT-A (for aneuploidies or abnormal numbers of chromosomes)
- PGT-M (for monogenic or single-gene conditions)
- PGT-SR (for structural rearrangements)
Find out more about how PGT can increase IVF success by choosing the healthiest embryos.
Lifestyle and Epigenetics: Genes Aren’t Everything
Genes lay the groundwork, but your lifestyle determines how genes act—this is epigenetics. Environmental influences can change gene expression without changing the DNA sequence itself.
Key Epigenetic Influencers:
- Diet (particularly folate and antioxidants)
- Exercise
- Toxin exposure (e.g., smoking, BPA)
- Stress
- Sleep patterns
Taking control of your health can not only enhance fertility, but also the health of your future offspring.
Dealing with Genetic Infertility: What Are Your Choices?
Whether genetic issues are affecting your fertility, there are many avenues to parenthood.
Reproductive Choices:
- IVF with ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) – of use in male factor infertility.
- PGT with IVF – Chooses embryos which are free from known genetic abnormalities.
- Egg or Sperm Donation – An option when gametes possess high-risk genetic characteristics.
- Surrogacy – When uterine or systemic issues make pregnancy difficult.
- Adoption – A kind, life-giving way to expand your family.
Our staff at Trinity IVF Ahmedabad guides individuals and couples through these decisions with compassion, experience, and cutting-edge care.
Final Thoughts: Knowledge is Power in Your Fertility Journey
Genetic influences on fertility do exist, but they are not a roadblock. Knowing whether you inherit infertility—and how it is expressed—may be the initial step toward successful treatment and good decision-making.
Genetic evaluation, counseling, and targeted therapies are closer than ever. If you’re experiencing difficulty with fertility and suspect that a genetic component may be at play, don’t delay seeking answers.
Take the Next Step with Expert Guidance
If genetic causes of infertility are what are concerning you, then Trinity IVF Ahmedabad has comprehensive assessments, state-of-the-art diagnostics, and empathetic care to guide you on your path.
Reach out to us today to book a consultation or discuss your possibilities with our fertility experts.