LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY
Surgery is a very important procedure when it comes to treatment of certain medical conditions. Although, with the increased risks associated with open surgery, there has been a need to move away from these highly invasive treatment procedures. One of the less invasive medical procedures that are being used by doctors today is Laparoscopic surgery. Though a surgical procedure, it makes use of fiber optic technology to diagnose and treat affected internal organs via a smaller incision thus reducing the risk of hemorrhage, pain, and recovery period.
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
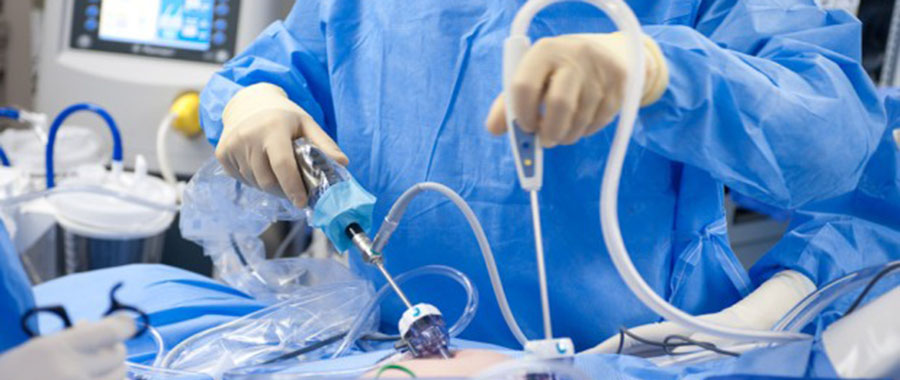
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows the surgeon to have a look at the inside of the abdomen or pelvis via a tiny incision, measuring 0.5 to 1.5 cm. Otherwise referred to as minimally invasive surgery (MIS), keyhole surgery or bandaid surgery, laparoscopy is a surgical procedure in which a telescope is inserted into the abdomen through a small cut below the navel. Attached to the laparoscope during this procedure are a camera, a cold light source, and surgical instruments. The cold light source, preferably Xenon or Halogen illuminates the affected area to enable the camera to take clear images of the organs and transmit them onto a television monitor. In addition to viewing the inside of the patient’s abdomen or pelvis, the doctor can also obtain biopsy samples and even perform minor or major surgical procedures.


How Does Laparoscopic Surgery Work?
The Procedure
Preparation
Just like any other surgical procedure, the doctor will perform blood tests, X-rays, urinalysis, electrocardiograms, CT scans, MRI scans and ultrasounds to diagnose any underlying conditions. This is mainly to determine if laparoscopy is the only diagnostic or operative option left. This step will also help in the detail planning of the laparoscopic surgery and the type of anesthesia required for that particular women.
Administration of Anesthesia
For this type of procedure, the patient is often put under general anesthesia so they can sleep through the whole procedure. In cases of minor laparoscopy, local anesthesia may be used to numb only the affected area while the patient stays awake during the procedure. It can also be done under the regional anesthesia depending upon the type of surgery
Laparoscopy
To begin with, the abdomen area is cleansed and prepared for the procedure. Then an instrument may be placed in the uterus through the vagina.to help the manipulation of the uterus Then abdomen is insufflate with the help of carbon dioxide. This makes space by pushing the abdominal wall and the bowel away from the organs in the pelvic area and makes it easier to see and operate on the reproductive organs clearly.
The surgeon will then make one or more incisions on the abdomen. These incisions measure between 0.5 and 1.5 cm. The laparoscope, which is a slender tube, like a miniature telescope, is then inserted through this incision accompanied with a cold light and surgical tools. The cold light illuminates the inside of the affected parts for better capturing of the images by the camera and transmitting it onto the monitor.
Through laparoscopy, the whole pelvis is cautiously scanned and the organs like the uterus, the fallopian tubes, the ovaries and the lining of the abdomen, called the peritoneum is inspected thoroughly. Apart from looking for infections affecting these structures, the surgeon also looks for adhesions , endometriosis and tubercles. In the case of abnormalities, the doctor can also obtain biopsy samples and even perform minor surgical procedures.
Stitching of Incisions
After the procedure, the laparoscope, lights, and surgical instruments are removed from the affected area and the gas pumped out. The incisions are then stitched and dressing applied. Since the incisions are so small, often stitches are not needed and they can be closed with Band-Aids.
Recovery
After surgery, the patient’s vitals such as breathing and heart rate are monitored closely. Depending on this, the patient may go home after several hours or spend the night in the hospital. There will be some pain and discomfort in the operated area, but generally, recovery is often within a couple of days. The patient is usually given medication to help relieve pain.
Whom Will Laparoscopic Surgery Benefit?
Laparoscopic surgery has been in use from as early as the 1900s, with much better techniques developed during the 1960s. Ever since laparoscopy has been successfully used to diagnose and even operate on a wide variety of areas. Patients who may benefit from this medical procedure include those suffering from conditions dealing with:
Gynaecology
This is the study and treatment of any conditions affecting the female reproductive systems. Some of the conditions diagnosed and treated under this category include conditions of the uterus, pelvis and reproductive organs. Some of these conditions include:
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)-This is a condition that causes small cysts to grow on a woman’s ovaries due to hormonal imbalance. PCOS is one of the common conditions known to cause infertility. 4 punctures per ovary are done to improve the ovarian hormonal environment for the development of good quality eggs
- Endometriosis-Women suffering from endometriosis usually experience a painful disorder where the endometrium, the tissue lining the inside of the uterus, grows outside the uterus. This condition usually occurs on the ovaries, fallopian tubes as well as the tissue lining the pelvis. This often causes cysts called endometriomas on the ovaries and abnormal bands of fibrous tissue, severe pain especially during periods and even infertility. As a treatment option, surgery may be recommended, and definitely, laparoscopic surgery makes an ideal option. Where these cysts are removed but the ovaries are preserved that too without any big cut on the tummy.
- Ovarian cysts- These are sacs filled with fluid that develop on a woman’s ovaries. While normal cysts disappear without treatment, when severe, they can rupture and cause pelvic pain, irregular periods, bloating and problems with fertility. Laparoscopic surgery may help the doctor know how severe the ovarian cysts are, and also in removing these cysts in the same anesthesia
- Fibroids-These are abnormal growths that often develop inside or on the outside of a woman’s uterus. While genetics, age, and hormonal imbalance are believed to cause fibroids, it is a condition that should be treated promptly as it could cause infertility. Laparoscopy is actually the best diagnostic and treatment option for this condition.
- Tuboplasty/Fallopian tube reconstruction- This is a treatment option for tubal infertility, with the aim of attempting to restore the patency and functioning of a woman’s fallopian tubes. It is mostly performed before Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI) and laparoscopy is the least invasive and most effective method to have it done.
- Tubal Recanalization- When a female has already undergone sterilization process and she comes for having a child again by natural means like in cases of remarriage or death of a child
- Adhesiolysis- This is a surgical procedure performed to divide or remove adhesions caused by bands of scar tissue during healing of surgery, infections, radiation, pathologies and trauma. Adhesions may appear as thin avascular sheets of tissue or thick vascular bands. Rather than open surgery, laparoscopic surgery may be used for adhesiolysis as it is less invasive.
- Adhesiolysis- This is a surgical procedure performed to divide or remove adhesions caused by bands of scar tissue during healing of surgery, infections, radiation, pathologies and trauma. Adhesions may appear as thin avascular sheets of tissue or thick vascular bands. Rather than open surgery, laparoscopic surgery may be used for adhesiolysis as it is less invasive.
- Corrective surgery for uterine malformation- With the correct tools, laparoscopic surgery can be of great help in performing surgery to correct uterine malformations such as bicornuate uterus, 2 horns of the uterus can be combined into one and congenital abnormalities among others.
For diagnostic purposes, laparoscopic surgery is greatly essential when performing a procedure known as Chromoperbutation. To check the status of fallopian tubes which is very important for planning IUI
-Chromoperbutation is a procedure performed by instilling dye through a woman’s fallopian tubes to access tubal patency. The dye used in Chromoperbutation is methylene blue and it is instilled through a transcervical cannula and its spillage observed from both tubes, which indicates tubal patency. For the best observation of this, laparoscopy is a necessity. Laparoscopy has many advantages over HSG as it also tells about adhesions, endometriosis, tuberculosis, relationship between tubes and ovaries and many other things
Urology
This is the study and treatment of any conditions that affect the urinary system. The main areas where laparoscopy is used include the bladder and the kidneys.
Advantages of Laparoscopy over open surgery.
- Laparoscopy is less invasive as compared to open surgery.
- Laparoscopy reduces the risk of excessive bleeding as compared to open surgery as the incisions made are much smaller.
- Laparoscopy reduces the risk of infection as compared to open surgery. This is because laparoscopic surgery reduces exposure of the internal organs being operated from external contaminants.
- Laparoscopy is normally done as an outpatient procedure. This means that you will be able to go home the same day as your surgery.
- A speedy recovery is achieved by laparoscopic surgery, mainly due to the smaller incisions made as compared to open surgery where very large and deep cuts are made. This reduces the length of hospital stay by a great deal.
- When compared to open surgery, laparoscopic surgery leads to much lesser pain and smaller scars. This is because laparoscopy involves the use of tiny incisions to access internal organs of the body unlike open surgery where large and deep incisions are used, leaving large scars and a lot of pain.